Local Search visualisation on 8 Queens Problem
Posted on February 19, 2023
The 8 Queens problem is a classic puzzle that involves placing 8 chess queens on an 8x8 chessboard in a way that none of the queens threaten each other. This project utilizes ReactJS to provide a visual representation of the local search algorithm solving the 8 Queens problem.
Built using
- React Js
- Javascript
- HTML
- CSS
Live

Background Information
8 Queens Problem
The 8 queens puzzle is a classic and challenging problem that requires placing eight chess queens on an 8x8 chessboard in such a way that no two queens are attacking each other. A queen can attack other pieces if they are placed in the same row, column, or diagonal. Therefore, the main goal of the puzzle is to find a solution that places the queens on the board without any of them sharing the same row, column, or diagonal.
However, solving the 8 queens problem can be computationally expensive due to the sheer number of possible arrangements. In fact, there are more than 4 billion possible ways to arrange 8 queens on an 8x8 grid, and only 92 of them are valid solutions. This makes a bruteforce search approach impractical since it has an exponential time complexity.
Local search
The local search algorithm is a heuristic approach that initiates with a random state and gradually improves it by making small changes to the present state in such a way that the new state has less cost than the current state. This process is repeated until it finds the optimal solution. The local search algorithm may not always produce the optimal solution due to the possibility of getting stuck in a local minima/maxima state.
The local search algorithm is useful for solving problems where the goal is to find the best solution by either maximizing or minimizing a cost value from a set of candidate solutions. These algorithms are applied to many hard computational problems, such as the TSP (travelling salesman) problem.
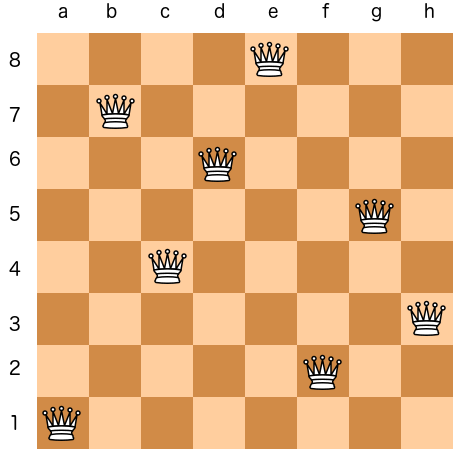
Initial State
The algorithms starts by randomly placing a queen in each of the column on the 8x8 chessboard as shown in the image above. This is the initial configuration where the search starts and moves towards a better configuration. As you can see, the current configuration contains queens sharing same rows and diagonals. This gets accomulated in the total cost of the current configuration which is shown at the top of the chess board. The goal here is to bring the total cost of the configuration down to 0. The local search algorithm does this by exploring the neighboring states and moving to one with cost less than current.
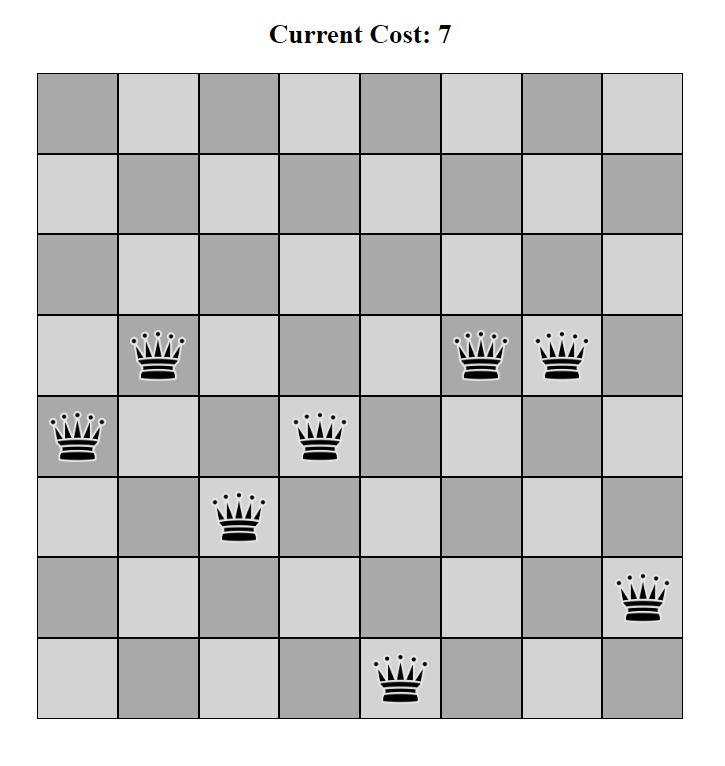
Neighboring States
A state refers to one specific arrangement of all the possible configurations of 8 queen pieces on a chessboard. To obtain a neighbouring state from any given setup, you can move one of the queen pieces vertically in a column. This means that each possible configuration can have up to 64-1 neighbouring states.
Getting stuck in local minima
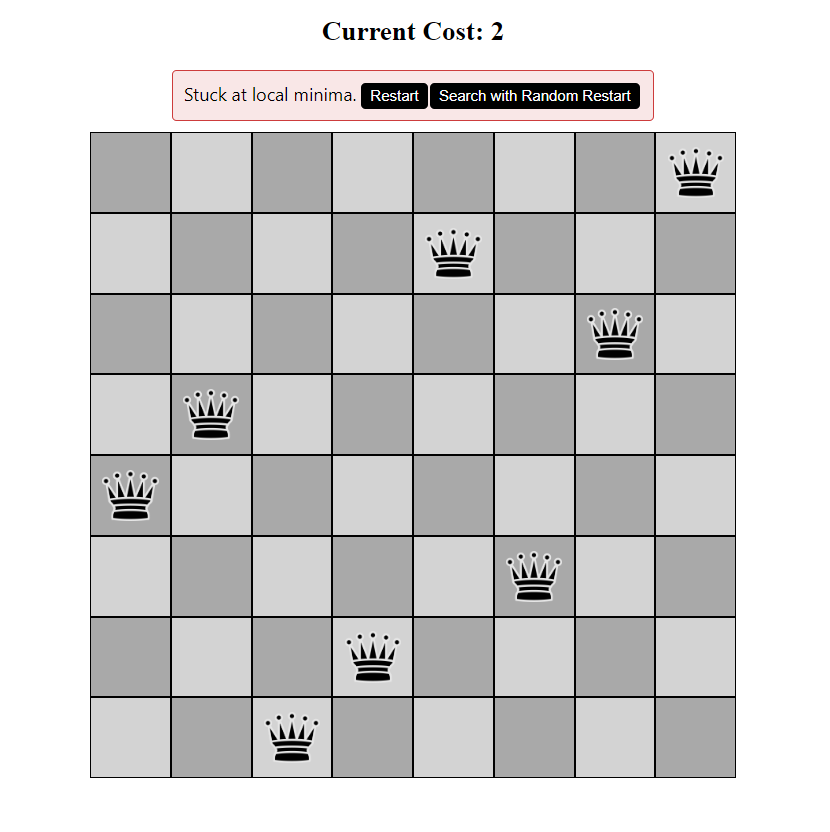 In mathematics, a local minimum is a point on a curve or surface that is lower than all nearby points but may not be the lowest point globally. Local minima can be found in various optimization problems.
In mathematics, a local minimum is a point on a curve or surface that is lower than all nearby points but may not be the lowest point globally. Local minima can be found in various optimization problems.
The local search algorithm employs a heuristic approach to find the optimal solution for a given problem by iteratively exploring the search space. However, it has a drawback of getting trapped in a local minimum, which refers to a state where the algorithm cannot improve the solution further as all the neighbouring configurations have a higher cost than the current state. This can lead to suboptimal solutions and hence, it is essential to incorporate strategies to escape local minima and explore other parts of the search space. A simple but naive strategy to reach an optimal solution is to restart it with a new random initial state.
Random restart
The random restart is a simple approach to get out of local minima. When the algorithm reaches a point where there are no better neighbouring states, it generates a new configuration randomly and starts working towards finding the optimal solution. This technique helps to avoid getting stuck in a suboptimal solution and increases the chances of finding the best possible solution.